Patellar tendinopathy and Infrapatellar bursitis
Distinct clinical features between patellar tendinopathy and infra patellar bursitis.
Patellar tendinopathy also known as jumper’s knee is a condition characterized by degeneration and inflammation of the patellar tendon. It commonly affects athletes involved in jumping sports such as basketball and volleyball. The primary symptom of patellar tendinopathy is localized pain and tenderness just below the knee cap. The pain is typically aggravated by activities that involve jumping or squatting. Patients may also experience morning stiffness and pain with prolonged sitting or climbing stairs.
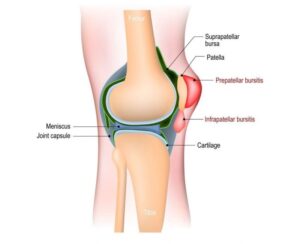
On the other hand infrapatellar bursitis also known as clergyman’s knee is the inflammation of the bursa located beneath the patellar tendon between the tendon and the tibial tuberosity. It is commonly observed in people who frequently kneel such as carpet layers and gardeners. The cardinal symptom of infrapatellar bursitis is focal swelling and tenderness below the patella. Unlike patellar tendinopathy the pain associated with bursitis is usually more diffuse and can be worsened by activities that put pressure on the knee such as kneeling or direct trauma.
Differential diagnosis between patellar tendinopathy and infrapatellar bursitis can be challenging due to overlapping clinical features. However a thorough history and physical examination can aid in distinguishing between the two conditions. As Licensed Massage therapist we should pay attention to the location and nature of pain aggravating factors and the presence of swelling or tenderness.
To further confirm the diagnosis diagnostic imaging techniques like ultrasound or MRI may be utilized. Ultrasound can assess the tendon structure and detect abnormalities such as thickening or neovascularization which are characteristic of patellar tendinopathy. MRI provides detailed anatomical visualization helping to identify signs of inflammation fluid accumulation or structural changes in both the tendon and the bursa.
Additionally other examinations such as plain X-rays may be performed to rule out fractures or other knee joint pathologies that could present with similar symptoms.
Once a definitive diagnosis has been made the treatment approach for patellar tendinopathy and infrapatellar bursitis may differ. Patellar tendinopathy is typically managed with a combination measures such as rest , physical therapy , Integrated Movement Specialist , Massage therapy and eccentric strengthening exercises.
In the case of infrapatellar bursitis the treatment focuses on reducing inflammation and relieving symptoms. Conservative management options include rest avoidance of aggravating activities,Heat, anti-inflammatory medications and the use of padding or protective knee sleeves. In more severe or chronic cases aspiration of the bursa fluid or corticosteroid injections may be necessary. To learn more about this, Or becoming an Integrated Movement Specialist (IMI) or Learn Massage therapy contact me at 630-968-7827 or email me at Info@sohmar.com
.